If you want to learn why the stock market goes through periods of extreme volatility, reruns of Pawn Stars shows you exactly why, several times each weeknight. Here’s how it works: Continue reading
Category Archives: psychology
Your Edge Comes With A Price
A few years ago, the Las Vegas Review-Journal conducted a six month survey of the payout percentages of selected nickel slot machines in 70 Las Vegas casinos. The payout rates ranged from a low of 86.86% to a high of 93.42%. It should come as no surprise Continue reading
Can Risk Management Boost Returns? Hint: Yes
This is the second of two emails I recently sent to my fellow finance committee members (of a local non-profit organization). The topic we have been discussing is the investment performance of the organization’s endowment. The points in this message apply just as much to retirement investors as they do to charitable endowment or foundation investors…
One last comment on endowment returns and strategy. Our discussions of managing risk shouldn’t be taken as code for “willing to accept small returns.” The truth is, playing defense can be an effective way to boost returns.
Winning strategies almost always contain an element of sacrifice. A football team will run the ball, repeatedly and ineffectively, to open up the passing game later. Casinos offer gigantic progressive jackpots to lure you into a bank of slot machines. Letting small forest fires burn naturally can prevent hugely destructive fires later.
One factor that allows roundabout strategies like these to work is the difficulty of pulling them off. Fans yell at you for calling plays like a moron. Paying out a big jackpot wrecks the slots manager’s P&L for a few days. Sacrifice, even when it’s well thought out and planned in advance, almost always feels wrong while it’s happening.
To most investors, the obvious route to better performance is through more aggressive concentration in growth assets. You can make a lot of money doing this, the hard part is keeping it. The less obvious strategy is being willing to sacrifice, what looks like easy money now, in return for gaining the earning potential of playing defense. Of having some way of avoiding large losses in order to allow more capital to be conserved and available for compounding.
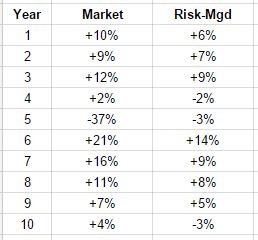
For example, let’s compare a set of hypothetical market returns to a set of hypothetical returns from a risk managed approach:
In this illustration, the market outperforms the risk-managed portfolio in nine out of ten years, some of those years by quite a bit. The managed portfolio has three negative years compared to only one for the market. Part of the reason for the persistent lag in the managed account is undoubtedly due to fees, so obviously the value of management is in question. But when you run the math over the entire period:
- Market total return = +50%
- Risk-Mgd total return = +60%
The moral of the illustration is that it’s not how often you match or beat the market that matters, it’s when you do it and by how much. In this example, playing defense in year five more than makes up for the relatively meager performance in every other year.
If our committee had coordinated the Risk-Mgd approach above, it would be easy to look back at ten years of completed returns and feel smug about the wisdom of it all. But in the real world, we would probably have spent 90% of the time feeling frustrated and talking about making changes.
I think the key for us is to not care about the market. Our focus should be on preserving and growing the endowment and doing our best to ensure that it can support the mission of the club when it needs to. That’s the only benchmark that really matters.
Disclaimer: The above example is hypothetical and is for illustrative purposes only. No specific investments were used in this example. Actual results will vary . Past performance is not indicative of future returns. Information displayed is taken from sources believed to be reliable but cannot be guaranteed. All indices are unmanaged and investors cannot invest directly into an index. Ideas and opinions expressed in this article are the sole responsibility of Patrick Crook/PLC Asset Management and do not reflect any stated opinions of LLP Financial LLC or any other person or entity.
You Are Lying To Yourself
We all do it. Consciously or not, we all lie to ourselves and it costs us money.
“The majority of your beliefs, particularly in business, are driven by what you want to be true.” -Tom Asacker, author of The Business of Belief
We form beliefs about things based on experiences and perceptions that are often just fragments of reality. An initial impression or a bit of passed down wisdom that we’ve heard from a young age can have an enormous and long-lasting effect on our expectation of how things are supposed to work. This leads us to mainly see only what we already believe and discount things that challenge those beliefs. It’s called confirmation bias and it’s probably costing you money right now.
For example, let’s say you’re Continue reading
The Strategic Investor: Part IV, Take Control by Letting Go
There are two recurring themes in a lot of these articles:
- Blind allegiance to the stock market can be dangerous.
- The wiring of our brains works against us as investors.
If the market wasn’t risky we wouldn’t need to worry about our faulty wiring because we wouldn’t have to make any decisions. If we were naturally suited to making good investment decisions under stress, a risky market would be less worrisome. However, the market is risky and our wiring is faulty – we need a strategy to deal with both. Continue reading